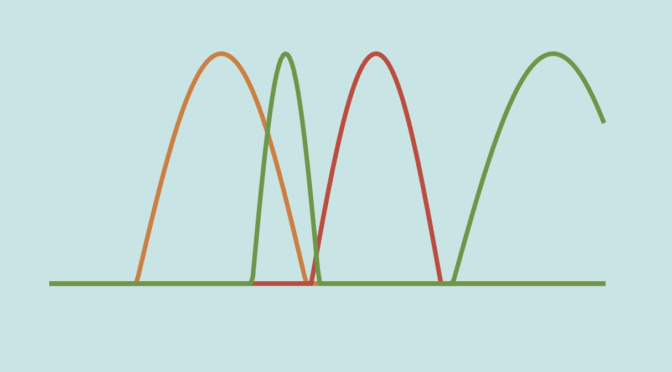
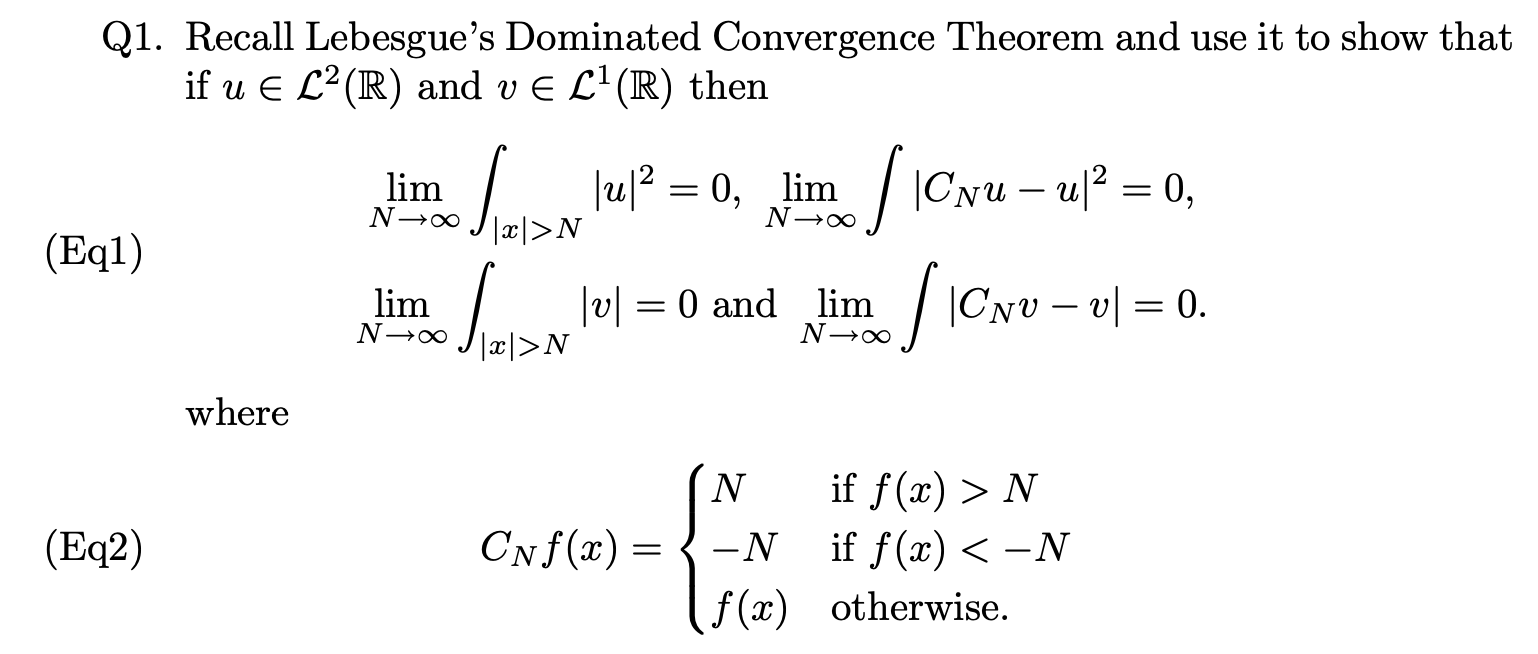
real analysis - Showing that Lebesgue Dominated convergence theorem is false in case of Riemann integration. - Mathematics Stack Exchange
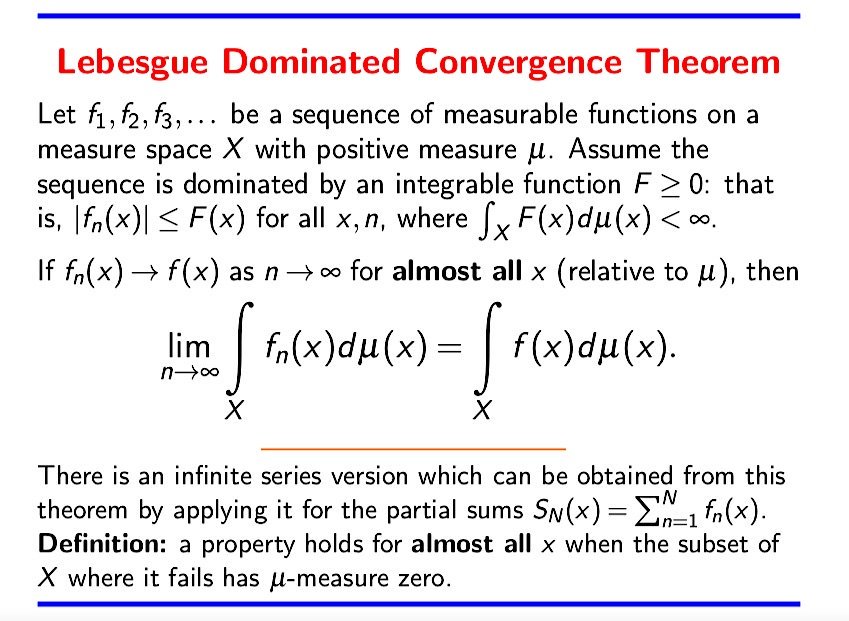
Sam Walters ☕️ on X: "The #Lebesgue Dominated Convergence Theorem (circa 1908). What I like about it is we don't need the stronger uniform convergence at each point, but merely pointwise convergence

SOLVED: Lebesgue's dominated convergence theorem extends the idea of interchanging limits and integrals to lim fn(c)dx = lim fn(r)dz, with a, b ∈ ℠∞ and n ∈ ℕ and fn converges

real analysis - An inequality in the proof of Lebesgue Dominated Convergence Theorem in Royden's book. - Mathematics Stack Exchange

fa.functional analysis - A question about PDE argument involving monotone convergence theorem and Sobolev space - MathOverflow

MathType on X: "Lebesgue's dominated convergence theorem provides sufficient conditions under which pointwise convergence of a sequence of functions implies convergence of the integrals. It's one of the reasons that makes #Lebesgue